In April 2021, the personal data of more than half a billion Facebook users worldwide was leaked online for free in a hacker forum. Personally identifiable information, full names, emails, phone numbers, Facebook IDs, locations, birthdates, and bio descriptions of Facebook users from 106 countries were exposed. Malicious actors scraped the data by exploding a now-defunct feature on Facebook that allowed users to find each other by phone number.
Cyber security is becoming a significant concern for businesses of all kinds as sophisticated strategies by cyber attackers continue to disrupt firms. Did you know that cybercrime costs organizations $2.9 million every minute? Major companies lose $25 per minute due to data breaches, according to RiskIQ Research. A study by IBM states that finding and containing the average cyberattack takes 280 days, and the average attack costs $3.86 million.
Let’s know all about cybersecurity in 5 easy points!
What is cybersecurity?
The technique of protecting computers, servers, mobile devices, electronic systems, networks, and data from hostile intrusions is known as cyber security (Types of Cyber security). It’s also known as electronic information security or information technology security. The phrase is used in various contexts, ranging from business to mobile computing, and it may be broken down into a few categories.
Significance of Cybersecurity
Data Protection:
Amidst digitalization, cybersecurity services safeguard sensitive data like personal, financial, and intellectual property from unauthorized access and theft.
Attack Prevention:
Efficient cybersecurity thwarts various cyber threats such as Malware, Ransomware, Phishing, and DDoS attacks, averting disruptions, data breaches, and financial losses.
Critical Infrastructure Security:
Essential services like power grids and healthcare heavily rely on interconnected systems, necessitating protection from cyber threats to ensure uninterrupted operations and uphold public safety and national security.
Business Continuity:
By preventing or minimizing cyber attacks‘ impact, cybersecurity service providers safeguard businesses from revenue loss, reputational damage, and potential closure, ensuring continuity in operations.
Regulatory Compliance:
Industries are mandated to adhere to stringent regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS to safeguard data. Cybersecurity ensures compliance, averting hefty fines and legal ramifications.
National Security:
By fortifying critical infrastructure, government systems, and military installations, cybersecurity plays a vital role in thwarting cyber threats and preventing cyber warfare, thereby safeguarding national security.
Privacy Preservation:
Information security services companies preserve organization’s data by protecting it from unauthorized access, surveillance, and misuse, fostering trust in digital services.
Exploring Some Common Cybersecurity Myths
Despite the increasing volume of cybersecurity incidents worldwide and the insights gained from them, persistent misconceptions pose significant risks.
While strong passwords offer some protection, they are not sufficient on their own. Cybercriminals can steal or purchase passwords, underscoring the need for additional security measures.
Contrary to the belief that all cyberattack vectors are contained, cybercriminals constantly discover new methods, targeting various systems like Linux, OT, IoT devices, and cloud environments.
Many falsely assume that certain industries are immune to cyber threats. However, every sector faces cybersecurity risks, with adversaries exploiting vulnerabilities in communication networks across government and private organizations.
Types of cybersecurity threats
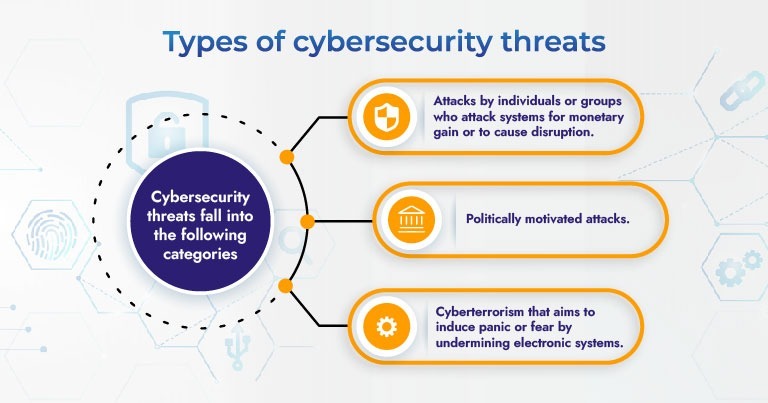
Types of cybersecurity:
- Critical infrastructure security
- Application security
- Network security
- Cloud security
- Internet of Things (IoT) security
Cybersecurity best practices:
Determine current cybersecurity posture: Prioritization is essential for a successful transformation plan to be implemented. Companies should be able to identify the potential sources of attacks, improve the present security measures for employees and customer intellectual property data, and consider the regulations.
Use a people-centric security practice: People can either be your most dangerous security threat or your most effective security protection. Since hackers frequently employ people as an entry point, a technology-centric approach to cybersecurity is no longer sufficient to offer all-around protection. As a result, it’s essential to take a people-centric strategy to manage human-related risks. In people-centric security, a critical perimeter is the workers themselves. Organizations must ensure all employees follow the cybersecurity practices recommended by your security policy. Educate the employees on the importance of following cybersecurity rules. Take regular feedback from the employees regarding the current corporate security system (how to combine robust security with an efficient workflow).
Back up your critical data: Cybersecurity management aims to reduce the reputational and financial effects of cyberattacks. As a result, companies should think about preventing data breaches and lowering the cost of successful breaches. Regularly versioning essential data and storing it in a separate location (hardware, for example) may assist firms in remaining functioning after a ransomware assault.
Implement the zero-trust cybersecurity paradigm: To get access to documents, the zero-trust cybersecurity paradigm requires that potential users, devices, and network systems be vetted. This is the most appropriate cybersecurity approach in today’s hybrid/remote working environment where device and network security is uncertain.
This approach involves the following:
- Introduce multi-factor authentication: Cyber-attacks often use hacked accounts to access a firm’s internal resources. Multi-factor authentication makes it difficult for hackers to access corporate data.
- Validating devices: Device identity and security, in addition to user identification, should be validated systematically.
- Minimize data access: Allowing employees access to as little data as they need to complete tasks (least access privilege) reduces the attack surface and, thus, the cost of successful breaches.
- Adopt micro-segmentation: To prevent computer viruses from spreading quickly (lateral movement), data should be stored in numerous micro-segments.
CASE STUDY
An energy company based in Germany was facing difficulty in monitoring and managing security policies on workstations and servers, implementing the SEP infrastructure, and aligning the policy configuration with the best practices. With the help of a leading cybersecurity provider, the company built a new SEP environment consisting of all workstations and servers and upgraded SEP clients to the latest version to fix critical vulnerabilities. It revised and configured the security policies as per the client’s best practices. The company was able to improve its security posture by blocking threats. It could detect and block over 8000 intrusion prevention events with sophisticated attack analytics within 6 months.
Conclusion
For any organization, a data breach can be damaging in many ways. The relevance of cybersecurity has progressively increased over time, to the point that executives outside of IT are taking note and prioritizing it.
What is the most important takeaway? Cybersecurity is a complicated process, and the best way to avoid assaults and secure your data is to use a multi-layered cybersecurity approach that knits together multiple technologies.
Looking for expert technology consulting services? Contact us today.





