The Evolution of Automation: From Manual Tasks to Intelligent Systems- Part 1
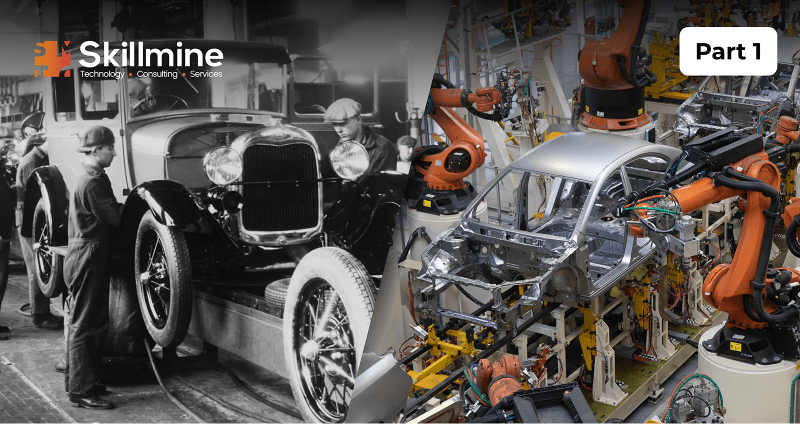
Overview
Half a century following Neil Armstrong’s manual piloting of Apollo XI to the moon’s surface, on March 24, SpaceX launched the colossal Starship rocket into space for its monumental third test flight. These remarkable strides owe much to automation including Robotic Process Automation, whose influence has intensified in recent years.
What is Automation?
Fundamentally, automation embodies employing technology to execute tasks with limited human involvement. It encompasses crafting systems or procedures that function autonomously, carrying out predetermined actions prompted by specific conditions, triggers, or algorithms. In essence, it entails delegating our tasks to machines. RPA solutions aim to streamline operations, minimize errors, boost efficiency, and optimize resource allocation.
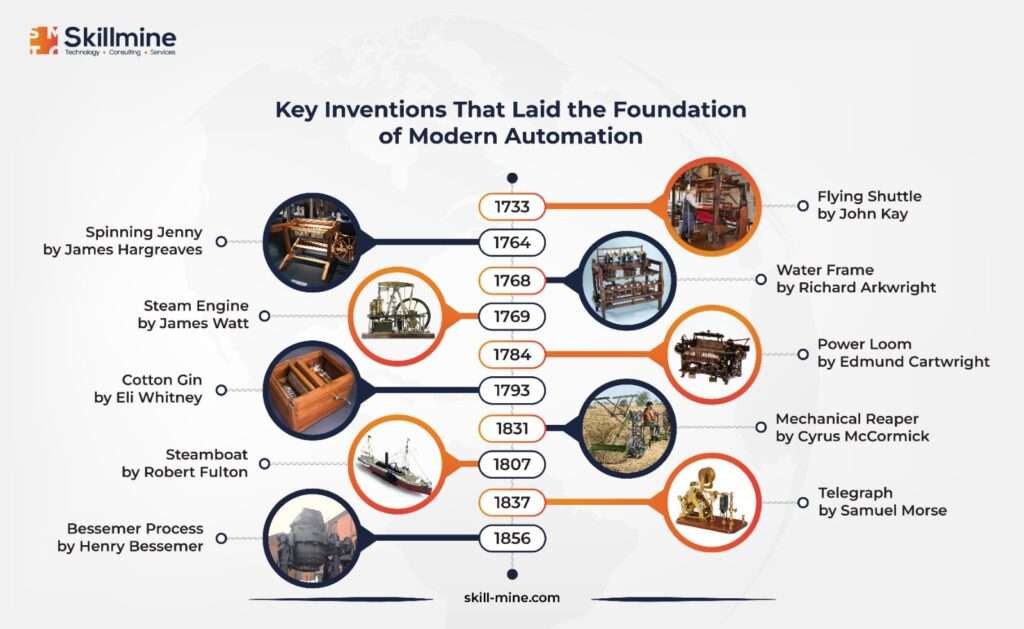
History of Automation
The origin of automation can be traced back to ancient times when humans devised tools to simplify their tasks. Examples of early automation , such as mechanical dolls and animals, are found in ancient civilizations like Egypt, Greece, and Rome. The Islamic Golden Age and various Chinese dynasties also contributed to the development of sophisticated automated systems.
In the late 1700s, the textile industry underwent mechanization by adopting power looms and spinning mills. However, the true transition towards industrial automation occurred during the late 18th century’s Industrial Revolution.
Automation in the Digital Age: A Paradigm Shift
During the mid-20th century, the emergence of the first programmable robots marked a significant milestone. The 1960s witnessed the debut of the inaugural industrial robot, while the subsequent decades of the 1970s and ’80s witnessed a proliferation of robotics and automation within the automobile manufacturing sector.
Nevertheless, the true revolution in automation unfolded during the latter portion of the 20th century, propelled by the rise of digital technology. Computers, microprocessors, and software paved the way for a transformative wave of automation that transcended the confines of manufacturing.
The 1960s saw the inception of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines, heralding a new era of automated control over machine tools. This breakthrough revolutionized the aerospace and automotive manufacturing industries, facilitating heightened precision and customization.
Subsequently, in the 1970s and 1980s, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) emerged as the cornerstone of industrial automation systems. These PLCs enabled real-time machine and process control, enhancing efficiency and reducing human error.
In recent decades, automation has undergone exponential advancement. Computers now govern and oversee a multitude of industrial processes. Service sectors have embraced self-service kiosks and online platforms, while homes have intelligent assistants and automated climate control systems.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands at the forefront, empowering virtual assistants, self-driving vehicles, automated stock trading, and a myriad of other applications, thereby ushering in a new era of unprecedented automation.
Conclusion
Automation’s transformative influence has been shaping the world for centuries, yet its momentum has surged notably in recent decades. Numerous technologies integral to our daily lives owe their existence to automation. As routine tasks undergo automation, the workforce must evolve, acquiring fresh skills. The essence lies in finding equilibrium: leveraging automation’s potential while safeguarding the invaluable traits of human innovation, compassion, and imagination.
Looking for expert technology consulting services? Contact us today.

