A leading healthcare network with numerous major hospitals wanted comprehensive vulnerability management while meeting industry and regulatory compliance requirements. The business also required to perform vulnerability scans within the guidelines of the PCI board, a time-consuming process considering the network size. The company approached SKillmine for a solution. We instituted an assessment methodology that met all the requirements posed by the client by creating a flexible vulnerability management approach. We could guarantee that time-consuming vulnerability scanning would be kept within a realistic duration by pre-populating the list of ports the vulnerability scanner was to scan.
The large-scale enterprise scan technique developed by Skillmine has proven to be a manageable strategy that integrates well with the client’s broader vulnerability and risk management programmes.
What is Vulnerability Management?
Vulnerability management is a continuous activity to analyse an organization’s security posture. Understanding each stage of the vulnerability lifecycle is crucial for organisations to protect themselves from newly discovered threats continuously.
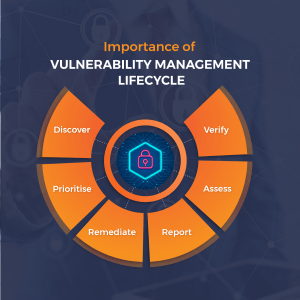
Importance of Vulnerability Management Lifecycle
Vulnerabilities can arise from changes in the operating environment, software bugs, configuration mistakes, and other factors. Cyber attackers can exploit these flaws to get unauthorised access to sensitive data.
Organizations can identify and prioritise vulnerabilities, create and implement a plan to resolve them, and keep an eye out for emerging vulnerabilities by implementing a vulnerability management lifecycle. This lessens the possibility of exploitation and safeguards against online risks. The vulnerability management lifecycle can also assist firms in meeting legal requirements, such as those pertaining to data security and protection.
Steps in the Vulnerability Management Lifecycle
Discover
The first step in the vulnerability management lifecycle is to identify and compile a list of all the assets that require vulnerability testing. These assets include software, web applications, operating systems, and hardware. It is crucial to fully explore all assets to avoid vulnerabilities in unmonitored systems or apps going unnoticed. All assets, including those unidentified or categorised as shadow IT, can be accurately accounted for with tools like network scanners, cloud management consoles, and asset discovery platforms.
Prioritise
In a vulnerability management program, it’s critical to prioritise which assets to concentrate on because not all assets are equally crucial to a company. High-priority assets are vital to regular business operations, are not fault-tolerant, or hold private information. Finding vulnerabilities in high-priority assets should be given more importance. The risk of compromise and the ensuing consequences can escalate if vulnerabilities in these crucial systems are not addressed.
Assess
Running conventional vulnerability scans with as much automation as possible is part of the assessment stage. This can be done by employing specialised tools that check online applications, cloud infrastructure, and other assets in the inventory for configuration errors and code vulnerabilities.
Once vulnerabilities have been identified, combine this data with the prioritised list of assets and any extra contextual data, such as the vulnerability’s risk assessment and the degree of exposure of the impacted assets. With the aid of this data, vulnerabilities can be prioritised for patching and appropriately reported.
Remediate
Remedial action is taken during the remediation phase to address a vulnerability, such as installing a security patch, upgrading hardware, or altering system settings. If quick, direct remediation is not possible, it may be necessary to reduce the chance that a vulnerability will be exploited until a fix can be implemented. One method would be to isolate a susceptible system from the rest of the network.
Verify
The verification phase, the last step in the vulnerability management lifecycle, is determining whether or not attempts to close vulnerabilities or mitigate their effects were successful. Given that enterprises must constantly scan and evaluate their IT infrastructures for vulnerabilities, this phase may overlap with the discover and assess stages of the following cycle. To confirm that remedial measures were successful, follow-up audits employing re-scans or penetration testing might be used.
Conclusion
Thus, organizations would be able to discover security loopholes, prioritise assets, assess, report, and remedy the weaknesses, and then confirm that they have been fixed using the Vulnerability Management Life Cycle. Skillmine has been helping businesses detect and mitigate risks with elaborate, well-charted vulnerability management strategies.
Looking for expert technology consulting services? Contact us today.