Across the globe, countries are implementing measures to heighten the security of individuals’ personal information. According to UNCTAD data, 66% of countries have established data protection laws. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) was introduced in 2018 to safeguard personal data across European Union member states. It establishes a higher bar for safeguarding consumer data rights.
Understanding GDPR
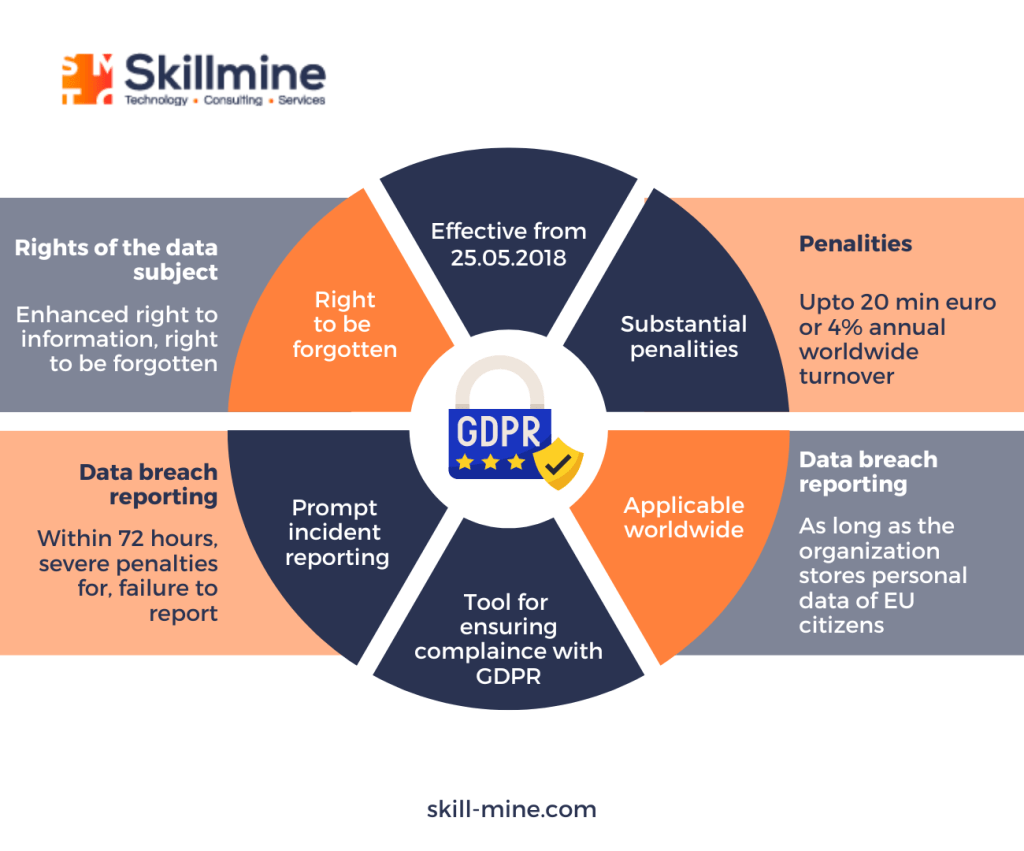
The GDPR constitutes comprehensive legislation with the primary objective of safeguarding, processing and movement of personal data, both within and beyond the European Union (EU). Although initially designed to protect personal data across EU member states, its influence is now global. In response, many countries are taking data privacy more seriously, prompting businesses to align with GDPR and formulate regional laws accordingly.
Understanding this regulation necessitates familiarity with key roles: a ‘controller,’ as defined in Article 4(7), determines data processing purposes, while a ‘processor’ (Article 4(8)) handles data on behalf of the controller. A ‘data subject’ is any identifiable natural person according to General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Article 3 of GDPR outlines its applicability, encompassing:
- Data processors and controllers operating within the EU.
- Data controllers and processors beyond EU borders offering goods or services to EU residents or profiling them.
- Entities processing personal data through EU-based branches.
In pursuit of protecting EU residents’ personal data, GDPR also exhibits extraterritorial reach, extending its scope beyond EU boundaries. Consequently, non-EU nations may fall under its purview. However, not all Indian businesses must comply with GDPR. Obligation arises for those Indian enterprises offering goods or services in the EU, processing EU-origin personal data, or profiling EU residents’ personal data.
How should Indian Businesses Comply with GDPR?
Once you have determined the applicability of GDPR to your Indian business, it’s crucial to take the following steps:
Update Your Privacy Policy:
- Specify Categories of Personal Data: Clearly list the types of personal and special data collected, including names, email addresses, addresses, religious or political beliefs, etc.
- Define Data Usage: Clearly state the purpose and lawful basis for data collection and processing, aligning with at least one of the six lawful bases outlined in GDPR.
- Secure Consent: Obtain explicit, free, and unambiguous consent from data subjects, empowering them with control over their data and privacy.
- Outline Data Subject Rights: Detail data subject rights, including the right to withdraw consent, restrict data processing, be forgotten, and request data portability, as per General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Safeguard Data Subject Rights:
Establish a mechanism to address data subject requests, including access, deletion, data processing restrictions, explicit consent, data portability, and rectification.
Determine Your Role – Data Controller or Processor:
Determine whether your business acts as a data controller, shaping data usage, or a data processor, handling data on behalf of others. GDPR Chapter 4 stipulates different obligations for controllers and processors, such as implementing technical and organizational measures.
Maintain Records of Data Processing:
Keep records if your business employs over 250 employees, in line with GDPR Article 30. Records should encompass:
– Data controller/processor names.
– Data collection purposes.
– Data types.
– Categories of data subjects.
– Recipient names.
– Processing activities conducted on behalf of processors.
– Documentation for data transfers to third parties or international organizations.
– Security measures for data processing.
Ensure Data Processing Security:
Employ technical and organizational measures to mitigate risks like unauthorized data access, loss, or alteration. Measures should include encryption, system and service confidentiality, integrity, and resilience, as well as regular testing and assessment of these measures.
Conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments:
Mandatory for businesses conducting systematic profiling, processing special or criminal offense data at scale, or systematically monitoring public places at scale. Assessments should include a systematic description of processing activities, necessity assessment, risk evaluation, and risk mitigation measures.
Create an Understandable Privacy Policy:
Craft a privacy policy that’s easily comprehensible, catering to individuals with varying levels of data protection knowledge. Offer translations in local languages if your business operates internationally.
Conclusion
Adhering to GDPR is of utmost importance for Indian businesses engaged with EU partners or operating within the EU to prevent potential fines and financial liabilities. In an era where individuals increasingly seek control over their personal data’s usage by businesses, GDPR compliance is paramount. It not only ensures trustworthiness but also fosters transparency and accountability, bolstering an organization’s reputation with its customers.
Looking for expert technology consulting services? Contact us today.










