An international construction group with markets across the USA and Europe wanted to prioritize profitability and IT risk management over growth. The company wanted a platform that helped it focus on qualitative and quantitative risk assessment, reporting capabilities and gave it the capability to foster collaborative teamwork.
Skillmine could bring risk identification, analysis and management on a single platform for the business. This helped the organization to make strategic decisions to tackle priority risks at a corporate level rather than on a smaller, disjointed project level.
What is IT risk management and why is it important for businesses?
With every step that your organization takes to enhance your digital transformation journey, you are foraying into more risks. The more open your business is, the more are enterprise risks involved. Businesses frequently run the danger of data breaches, technological failures, virus attacks, and cyberattacks.
Risks can be avoided by ensuring the following:
Confidentiality: Establish and implement the necessary permission restrictions to ensure that only users who require access have access.
Integrity: Establish and enforce controls to prevent the alteration of information without the consent of the data owner.
Availability: Create and implement safeguards to stop systems, networks, and software from becoming unusable.
IT Risk management
The process of identifying, evaluating, and controlling risks to an organization’s resources and profits is known as risk management. These dangers can be caused by a number of things, such as monetary unpredictability, legal responsibilities, technological problems, strategic management blunders, accidents, and natural calamities.
A successful IT risk management process takes into consideration the full range of risks an organization faces. The relationship between risks and the potential negative cascading effects on the strategic objectives of an organization are also examined by an organization’s IT risk management strategy.
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is the term used to describe the process of anticipating and comprehending risks across an organization. ERM, in addition to concentrating on internal and external threats, emphasizes the significance of managing positive risk. Positive risks are chances that, if taken, might boost a company’s worth or, alternatively, hurt it. Any risk management program’s goal is, in fact, to protect and enhance corporate value by taking calculated risks rather than to completely eradicate all risk.
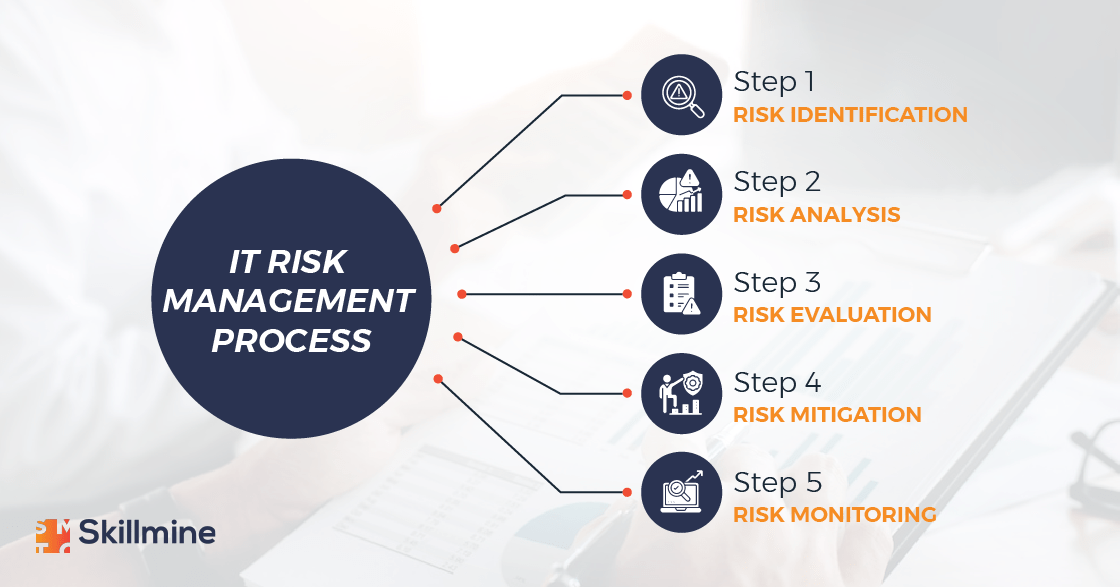
Risk identification: It is important to understand that something is a risk only if it has an impact. According to the NIST Interagency Report (NISTIR 8286A) on identifying cybersecurity risk in ERM, following are the factors that must be present for a negative risk scenario:
- A valuable asset or resource that could be impacted;
- A source of threatening action that would act against that asset;
- A pre-existing condition or vulnerability that enables that threat source to act; and
- Some harmful impact that occurs from the threat source exploiting that vulnerability.
The same four factors are applicable for negative risks as well.
Risk analysis: There is a need to understand that not all data are created equally. Personally Identifiable Information (PII) such as a person’s name, birth date, social security number, or even IP address are high-risk assets that are frequently targeted by malicious attackers.
Risk evaluation: Each data asset is located in a particular location. It is important to ascertain how each risk interacts with the others and influences the likelihood of an attack by an attacker. The most effective approach to achieve this is to calculate using the formula:
Risk Level = Likelihood of a data breach X Financial impact of a data breach
A low-risk data asset, like marketing content, might be in a high-risk place, like a file-sharing application. However, if a hacker steals the information, the financial impact on your business will be minimal. As a result, this might be considered low or moderate risk.
A high-risk data asset, like a consumer medical file, in a moderate-risk setting, like a private cloud, might have significant cost consequences. Thus, this would almost always be considered a high risk to your organization.
Identifying the types of data your organization stores and aligning that to the locations where you store your information act as the basis for your risk analysis.
Risk mitigation
A risk can be accepted, transferred, mitigated, or refused depending on your risk tolerance. Risk can be shifted by purchasing cyber risk liability insurance. Installing a firewall to block access to the site is another way of reducing risks.
Firewalls and encryption are examples of mitigating controls that serve as barriers to harmful actors. Even mitigating controls, nevertheless, occasionally fail.
Risk monitoring
Risks are ever-changing, and keeping an eye on them enables companies to operate smoothly. With technology constantly evolving and hackers discovering new loopholes to attack organizations, continuous monitoring of the system is the need of the hour.
Importance of IT risk management
- Provides protection to organizations from potential hackers by integrating risk management solutions.
- Eliminates threats and secures the employees’ jobs and customers’ information.
- Enhances communication within an organization by setting expectations and relating data to the company’s growth.
- Optimizes resources and ensures correct configuration in the company’s performance.
- Ensures the systems are updated regularly and ensures rapid recovery from any malware attack.
Conclusion
Since cyberattacks can take many various forms, what works for one data asset might not be effective for another. Hence an effective IT risk management program should be a combination of a diverse set of rules and techniques. In order to make sure that cybersecurity efforts stay up with the changing threat landscape, it is crucial that business security teams implement various IT risk management best practices. COMPLYment is an IT Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC) solution by Skillmine that combines these best practices. Know how COMPLYment can keep risks at bay for your business:
Looking for expert technology consulting services? Contact us today.





