As the demand for cloud computing continues to soar, businesses are embracing cloud migration services at an unprecedented pace. According to cybersecurity magazine Arcserve, the total cloud storage is expected to reach 200 zettabytes by 2025. As companies now prioritize the benefits of scalability, cost reduction, and swift application updates, it is essential to understand how to determine which applications are suitable for cloud migration.
Exploring Cloud Application Migration
Cloud application migration involves the transfer of software applications across various computing environments. This includes moving applications from a public cloud to a private cloud or transitioning them from a local server to a cloud environment. By harnessing cloud computing, organizations can unlock the advantages of enhanced scalability, cost reduction, and the ability to implement rapid application updates.
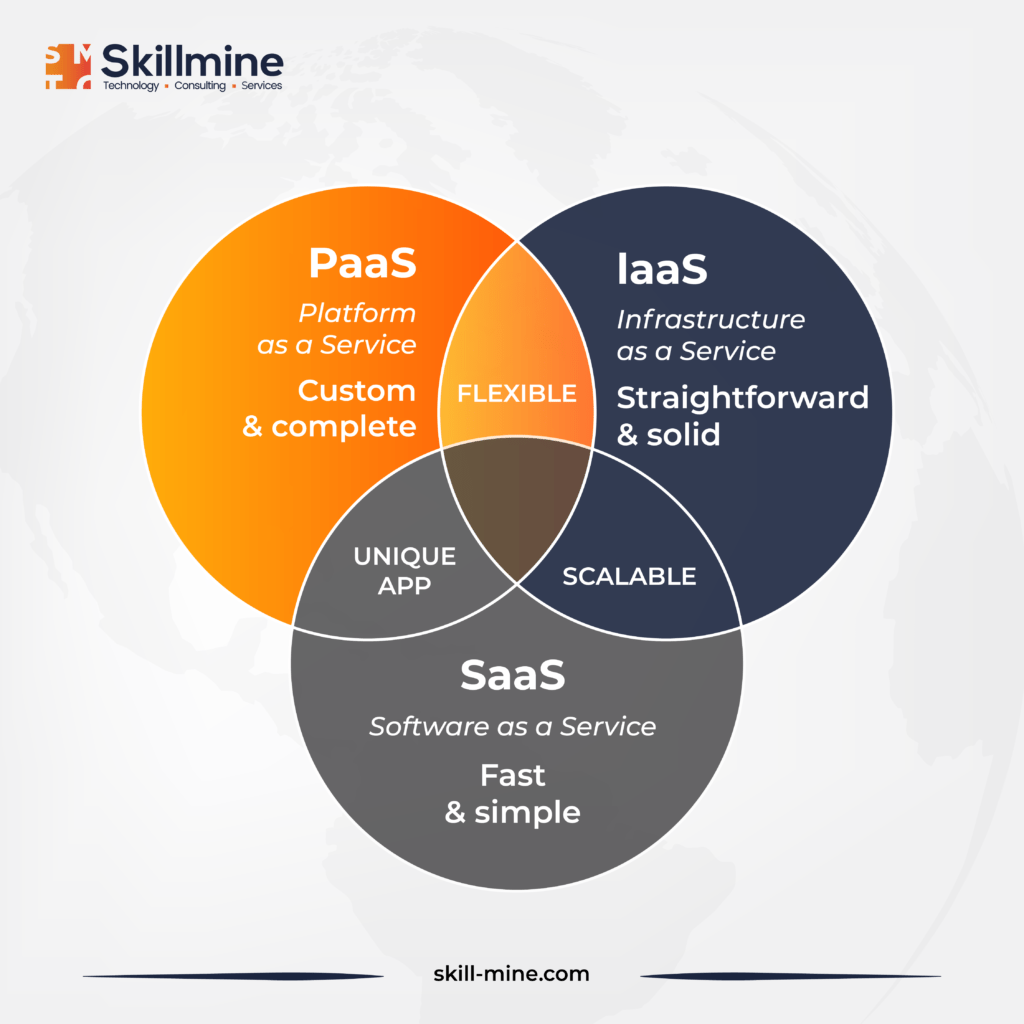
Understanding Different Cloud Migration Options
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS enables the relocation of infrastructure from traditional on-premises data centers to private or public clouds. By leveraging IaaS, businesses can optimize their applications with minimum customizations while eliminating the ongoing costs and responsibilities associated with on-premises infrastructure management. This approach allows for the retention of the existing licensing structure used on-premises.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS provides a cloud computing model where third-party providers offer software and hardware tools over the Internet, primarily catering to users in need of application development tools. In contrast to IaaS, PaaS doesn’t replace the entire IT infrastructure but rather offers an optimized environment for application development. Developers can focus on creating and running applications within this environment, alleviating the burden of managing basic services and infrastructure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS adopts a software licensing model where applications are hosted on external servers. In this subscription-based model, the cloud provider assumes full responsibility for application maintenance and updates. While SaaS offers convenience and configuration tailored to organizational needs, customization flexibility may be limited compared to on-premises applications. Additionally, certain custom developments may not seamlessly transfer to a SaaS model.
Factors to Consider When Evaluating Applications for Cloud Migration
- Application Criticality: For enterprises, it is advisable to begin cloud migration with low-risk, low-value applications while exercising caution with mission-critical applications. By prioritizing applications with minimal customer data or those benefiting from the cloud’s elastic features, businesses can mitigate potential risks. However, avoiding the migration of larger, mission-critical applications may hinder the full realization of cost savings and value inherent to the cloud.
- Cost Analysis: Conducting a comprehensive cost analysis is crucial when comparing on-premise applications with Software as a Service (SaaS) alternatives. While on-premise applications may appear expensive initially, SaaS applications offer a pay-as-you-go model that seems cost-effective. It is essential to consider maintenance costs, licensing fees, and ongoing subscription expenses to make an informed decision.
- Sensitive Data Considerations: Applications lacking sensitive data are ideal candidates for cloud migration, while those involving such data may require a hybrid cloud approach. Systems housing sensitive information, such as customer data and financial records, may face regulatory compliance and governance challenges, making cloud migration complex. Organizations should carefully evaluate the implications and choose an appropriate migration strategy.
- Integration Complexity: The complexity of migration often depends on the location and frequency of communication between applications and external systems. Standalone applications or those with batch integrations are generally well-suited for cloud migration. Conversely, applications requiring integration with data sources or legacy systems may experience challenges, such as latency issues. Applications with fewer dependencies are typically more suitable for seamless cloud migration.
- Legacy Apps and Customizations: A thorough assessment of existing systems is paramount to identify and exclude obsolete or heavily customized applications. Legacy applications often require extensive upgrades before cloud migration becomes feasible. Additionally, businesses relying on highly customized applications may face challenges in finding compatible cloud solutions tailored to their specific requirements.
Conclusion
While the cloud offers numerous advantages, it is essential to approach cloud migration thoughtfully and strategically. With careful planning, the right partners, and a well-defined strategy, businesses can leverage cloud migration services and transformation services to reduce costs, enhance productivity, make informed decision-making, and drive innovation. Contingency plans should be in place to address unexpected challenges. Choose Skillmine’s Cloud Transformation Services to seamlessly migrate from legacy, on-premises setups to public cloud-native storage while minimizing disruption to your business operations.
Looking for expert technology consulting services? Contact us today.





