In 2023, a nationwide credit reporting company was engulfed in a colossal data breach, compromising the personal information of up to 143 million Americans, including sensitive data like social security numbers and driver’s licenses. However, amidst the turmoil, the company remained silent for months, exacerbating the crisis. What should have been a proactive approach? A comprehensive plan should have been meticulously laid out for the crisis team, specifying their collaborative strategies, defining initial messaging and statements, and outlining escalation procedures. Regrettably, the company’s lethargic and mishandled response only worsened the situation. This begs the question: How should businesses navigate adversity effectively? Do technology consulting services companies have a role to play?
Understanding Crisis Management
Crisis management encompasses a strategic methodology aimed at aiding organizations in navigating unforeseen occurrences that pose a threat to the organization, its stakeholders, or the wider community. It entails proactive measures such as planning and simulations to anticipate potential crises, adeptly responding to crises as they arise, and leveraging lessons learned to enhance future responses. At its core, crisis management by IT Consulting Services companies is focused on mitigating crisis impact and promptly reinstating regular operations, thereby safeguarding the organization’s viability and upholding public confidence.
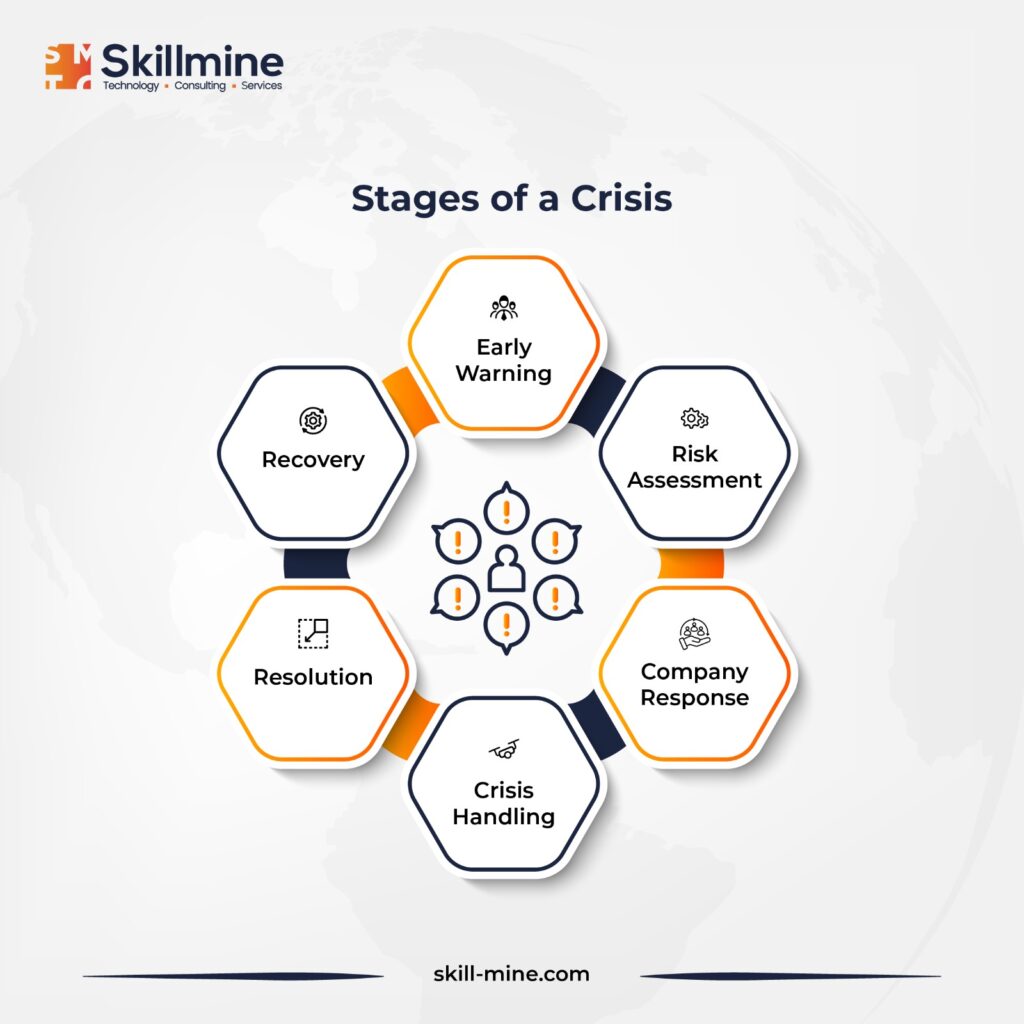
Importance of Crisis Management
Effective crisis management is crucial for businesses to safeguard their reputation and stakeholders, mitigate financial losses, and ensure business continuity. By implementing robust crisis management strategies, organizations can instil confidence in their customers, minimize the financial impact of crises, maintain essential operations through business continuity plans, and preserve public trust through transparent and empathetic communication. Regular testing and updating of mission-critical applications are essential for maintaining business continuity, while transparent and trustworthy communication during crises is vital for preserving public trust.
Goals of Crisis Management
Ensuring Safety and Well-being: Ensuring the safety and well-being of employees, customers, and stakeholders is the foremost objective of crisis management. This entails implementing emergency response plans, disseminating timely and accurate information, and taking necessary measures to mitigate risks and protect individuals from harm.
Minimizing Operational Disruptions: This involves necessitating the adoption of alternative work arrangements, activation of backup systems, and resource reallocation to essential functions. The aim is to maintain smooth operation of mission-critical applications while addressing challenges arising from the crisis.
Effective Crisis Communication: Organizations must establish transparent channels to keep stakeholders informed, address concerns, and provide updates on crisis response progress. Utilizing various communication platforms is key to reaching diverse audiences effectively. Establishing crisis communications hubs facilitates communication with stakeholders and relevant parties, such as suppliers and customers, streamlining information dissemination.
Preserving Reputation and Brand Image: This necessitates honest, transparent, and empathetic handling of the situation. Promptly addressing issues, taking accountability for mistakes, and implementing measures to rebuild trust are vital.
Learning and Adapting from Crisis Situations: Conducting comprehensive post-crisis reviews, identifying strengths and weaknesses, documenting lessons learned, and implementing improvements are crucial steps towards bolstering future crisis management capabilities and averting potential crises.
Best Practices for Crisis Management
Building a Crisis Management Team: An effective response hinges on the establishment of a specialized crisis management team, comprising seasoned professionals from diverse organizational departments. Endowed with clear authority and delineated roles, this team orchestrates a swift and coordinated crisis management effort, mitigating potential repercussions.
Risk Assessment and Warning Systems: Pre-emptive risk assessment and robust monitoring systems, such as advanced Information technology surveillance, are indispensable for identifying and addressing potential crises. These systems, spanning from mechanical to financial metrics, furnish early warning signals, facilitating timely intervention.
Developing Crisis Response Protocols: Proactive crisis management demands the establishment of clear incident management protocols encompassing defined roles, escalation procedures, and communication channels. The designated crisis manager spearheads response efforts, ensuring alignment with the Crisis Management Plan (CMP) and adeptly communicating with both internal and external stakeholders.
Utilizing Incident Management Software: Leveraging incident management software streamlines crisis response endeavors, offering a centralized platform for tracking and managing major incidents, facilitating task assignment, disseminating updates, and conducting data-driven analyses for future enhancements.
Post-Crisis Analysis and Adaptation: Following crisis mitigation, ongoing evaluation sessions, particularly involving legal and finance team members, assess recovery progress and provide stakeholders with timely updates. Concurrently, revisiting the CMP enables refinement based on crisis learnings, fostering organizational resilience.
Learning from Past Incidents: Each crisis serves as a learning opportunity, necessitating comprehensive post-incident reviews to identify process gaps and weaknesses. Documenting lessons learned and updating CMPs accordingly bolsters organizational readiness and fortifies against future crises.
Conclusion
Comprehensive crisis management by technology consulting companies extends beyond cyber incident response to encompass the entire lifecycle of readiness, response, and recovery. Coordinated and robust responses to incidents are crucial in minimizing damage and losses. Skillmine’s COMPLYment, an internally developed IT GRC solution, aids in risk mitigation and remediation efforts. COMPLYment simplifies the process of IT Risk Management for processes and assets in five cycles: IT risk assessment, IT risk evaluation/ identification, IT risk mitigation planning, IT risk review, and IT risk register.
Looking for expert technology consulting services? Contact us today.





