As businesses progressively transition towards cloud adoption, the significance of identity and access management (IAM) within multi-cloud landscapes emerges as a paramount concern. Based on findings from a study by Strata Identity and Forrester, a striking 78% of IT decision-makers emphasized that effectively managing user identities across multiple clouds presents their foremost challenge.
This prevailing encryption shortfall raises heightened apprehension, particularly in the context of multi-cloud environments, where both human and machine identities are accommodated. The management of machine identities and access across multi-cloud infrastructures has acquired profound significance. The compromise of machine identities renders machines susceptible, instigating costly data breaches.
Challenges Arising from IAM in a Multi-Cloud Setting
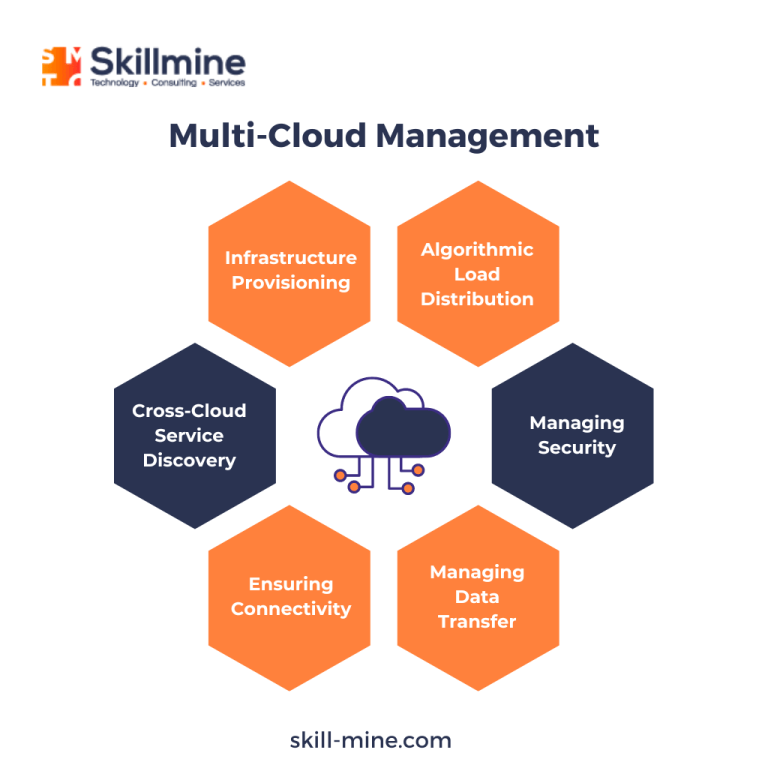
The secure implementation of IAM practices across a multi-cloud environment presents a host of intricate challenges. There are concerns stemming from the operational intricacies in effectively managing encryption and associated keys across diverse providers. Each provider possesses distinct consoles and APIs, compounding the complexity. Without a comprehensive grasp of the obstacles confronting machine IAM within the cloud, the formulation of a viable solution remains elusive.
Machine identities are experiencing a surge, outpacing their human counterparts. While many enterprises adeptly handle human IAM within the cloud, fewer possess the expertise to secure machine identities in a multi-cloud ecosystem.
IAM tools offered by public cloud providers exhibit limited scalability across various environments. Though numerous cloud architectures furnish in-house identity and access management solutions, their effectiveness diminishes when safeguarding multiple environments.
IAM tools predominantly govern access rather than activity. While various cloud-native tools offer privileged access management (PAM), they lack the capability to monitor or audit user or machine activity post-access.
The absence of a standardized multi-cloud security model exacerbates the situation. The current landscape lacks uniformity in securing hybrid or multiplatform environments. In the absence of a centralized IAM solution spanning platforms, duplication of efforts becomes inevitable.
The inherent security challenges within the cloud, such as identity and key sprawl, vendor lock-in, and governance deficits, further compound the complexity.
When contemplating additional cloud providers, specific security nuances need to be considered. The scenario of transitioning an instance from one provider to another necessitates seamless handling of keys and certificates. The division of key and certificate management among disparate third-party providers also poses concerns. Before embarking on a multi-cloud or hybrid journey with machine identities, assessing the following questions regarding certificate ownership is imperative:
- Are you at ease entrusting your keys and certificates to unfamiliar entities?
- What happens to your hosted digital identities when you change providers?
- Who ultimately retains ownership over machine identities when parting ways? Alternatively, do your identities span multiple public clouds, thereby amplifying the compromise risk?
IAM Solutions for Multi-cloud Environments
In the realm of IAM within multi-cloud environments, escalating complexity is brought in by each new cloud addition. Each one introduces distinct technological implementations, operational models, and security tools, thereby increasing management intricacies. Addressing each independently demands substantial resource allocation, which may still leave security vulnerabilities without coordinated management.
A robust multi-cloud IAM solution should exhibit the following features:
- Vendor agnostic: Cloud-native solutions struggle to keep up with the complexity of certificates across multiple platforms. Opt for one that enforces access controls based on identity rather than environment.
- Scalability: A cloud-agnostic approach mitigates vendor dependence and streamlines expansion to accommodate additional public cloud architectures.
- Comprehensive Visibility: Your chosen solution must offer comprehensive visibility into your environment’s keys and certificates, promptly adapting to newly deployed entities.
- Informed Intelligence: Your solution should provide all essential information for streamlined certificate lifecycle management. This includes expiry dates, organizational data, and security configurations.
- Automated Efficiency: Your solution should simplify operations and eliminate silos by embracing automated provisioning and renewal of certificates across all cloud architectures.
Conclusion
Skillmine’s cloud-agnostic solutions, orchestrate machine identity management across diverse public cloud architectures. By seamlessly integrating multiple platforms, our solutions not only bridge security gaps but offers a centralized, certificate management solution.
Looking for expert technology consulting services? Contact us today.