Did you know? Nearly 1 billion emails were exposed in a single year, affecting 1 in 5 internet users. As cybercrime increases, organizations adopt security measures like multi-factor authentication (MFA) to guard against credential theft, phishing, and password attacks. To get around this added layer of protection, hacking groups have developed a new tactic: MFA fatigue.
What is MFA Fatigue?
MFA fatigue, also referred to as MFA exhaustion, 2FA fatigue, MFA push spam, or prompt bombing, represents a tactic employed by hackers to evade multi-factor authentication while infiltrating user accounts. In contrast to other methods that exploit zero-day vulnerabilities, social engineering, active session hijacking, or man-in-the-middle attacks, MFA fatigue employs a brute force strategy. Attackers utilize stolen, leaked, or guessed credentials, persistently bombarding the account owner with verification prompts until they make a mistake, succumb to psychological pressure, or the attacker moves on.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
Multi-Factor Authentication is a method of credential authentication that necessitates users to provide multiple verification methods as evidence of their identity and the legitimacy of their credential access. One prevalent type of MFA is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA), which mandates two factors for authentication.
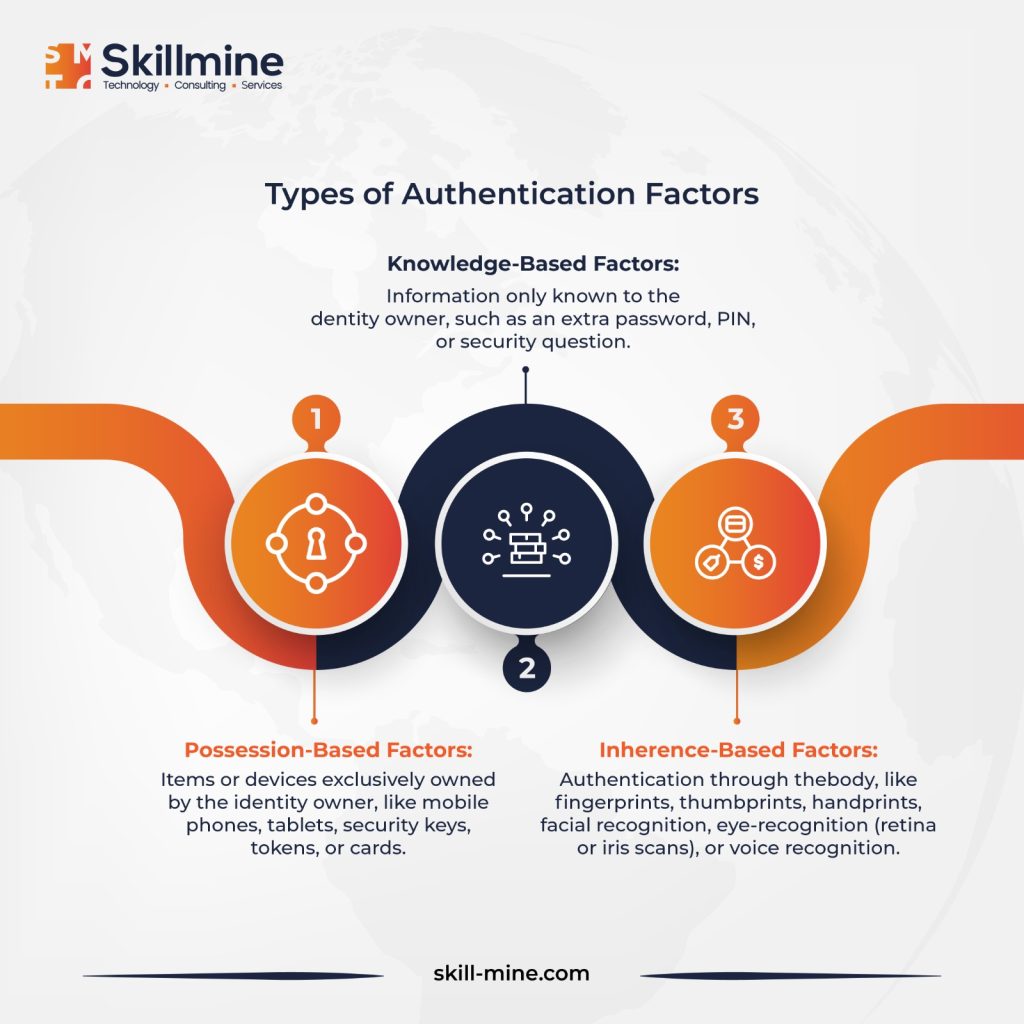
The MFA authentication process typically initiates at a login interface. Following the submission of proof of identity (the first factor), like a username and password, users are prompted to authenticate their identity further using at least one additional factor before gaining access to the resource. These authentication factors encompass a second password or PIN, biometric data, GPS or network location, or an object or device physically possessed by the user, such as a mobile device or security card – with the latter being more prevalent in contemporary MFA setups.
Upon logging into an application, system, or single sign-on portal, users receive a push notification on their authentication device. For most users, this notification originates from an application on their personal or work mobile device or a confirmation call or text to their phone number. This is the vulnerable area targeted by Multi-Factor Authentication fatigue attackers.
How does an MFA Fatigue Attack Start?
User Credentials and Information Collection
- MFA fatigue begins with obtaining user information, including usernames, passwords, or recovery credentials, often acquired through preliminary attacks like phishing, social engineering, or from exposed credentials in a breach.
Stolen Credentials Utilized for MFA Push Notifications
- Attackers use stolen credentials to sign in and activate push notifications for multi-factor authentication, bombarding the victim with rapid notifications on various platforms, such as email, text, or desktop, usually directed to the victim’s authenticated mobile device.
Victim Receives Push Notifications and Experiences “Fatigue”
- The victim receives a barrage of push notifications, aiming to overwhelm them. The attacker’s objective is to prompt the victim to confirm their identity by selecting “Yes,” allowing the attacker to gain further access. Victims may comply to stop the notifications, assuming a technical glitch, a test, or to end the annoyance.
- The attacker might impersonate tech support, contacting the victim and falsely explaining that the notifications are part of routine maintenance.
Securing Against MFA Fatigue Attacks: Best Practices
Optimize MFA Configuration:
- Reduce the time window for factor authentications.
- Limit unsuccessful access attempts and add geolocation or biometric requirements.
- Increase the number of required factors and flag misconfigurations.
Enhance User Education:
- Provide high-quality, frequent training on security protocols.
- Educate users to detect social engineering attempts and flag unsolicited push notifications.
Strengthen Password Management and Authentication Beyond MFA:
- Implement a Zero Trust approach and utilize FIDO2 authentication.
- Enforce least privilege access rights to restrict malicious actors’ movements.
- Apply web-based FIDO2 authentication for possession-based credentials.
Implement Least Privilege:
- Restrict access rights to essential resources for users, accounts, and processes.
- Limit the impact of attacks by minimizing privileged access.
System Hardening:
- Reduce the attack surface by eliminating potential flaws and backdoors.
- Keep security resources, software, and firmware up to date with the latest patches.
Expand Vulnerability Management:
- Detect and patch vulnerabilities in real-time through discovery, assessment, and remediation.
- Prioritize urgent vulnerabilities, correct them through patching, and log all activities for audit trail.
Conclusion
As the risks to data security grow and cybercriminals employ sophisticated tactics like MFA fatigue attacks, businesses need to enhance their defence against data breaches. Skillmine takes care of the security needs of businesses, shielding its tools, processes, and people through an uncompromising strategy backed by research. Our indigenous authentication and authorization solution, Auth, implements MFA and SSO, centralizing authentication and simplifying access management across multiple applications in an organization.
Looking for expert technology consulting services? Contact us today.





